"How to Calculate Reactive Power? How to Avoid Reactive Penalty?", we will be talking in detail about what reactive power is and how to avoid the reactive penalty we see in our invoices.
Reaktif Güç Nedir ve Neden Önemlidir?
Reactive power is a type of power in electrical systems and is often important in industrial electrical systems. This occurs due to the phase difference between voltage and current. Reactive power is different from active power. Active power is the real power that is used directly to do work (for example, the power required to turn a motor). Reactive power, on the other hand, is consumed or generated to correct the electric current when it is not in phase with the voltage.
Reactive power is caused by the presence of inductive or capacitive loads. Inductive loads (e.g. motors, transformers) consume reactive power, while capacitive loads (e.g. capacitors) supply reactive power. Reactive power is calculated together with real power to determine the total power consumption. Therefore, the control and management of reactive power is important for the efficiency and safety of electrical systems.
How is Reactive Power Calculated?
In order to operate the equipment such as transformers, motors, welding machines, UPS etc. in our enterprises, reactive current and accordingly reactive power is needed. These equipments need reactive power during their operation. After the end of operation, this power requirement they draw from the distribution network disappears.
Reactive power oscillation reduces the grid capacity as it occupies the grid unnecessarily. Thus, it causes heat loss in all electrical equipment. The distribution network has set certain limits on reactive power emission for consumers. As a result of exceeding these limits, the distribution network reflects a reactive consumption charge on the consumer's electricity bill at the end of the month. We call this reactive consumption charge "reactive penalty". How to Calculate Reactive Penalty? You can also read our article.
Compensation
EMRA has published the "Procedures and Principles Regarding Tariff Implementation of Distribution License Holders and Incumbent Supply Companies" regulation sets out precisely the circumstances in which a reactive penalty will be imposed and the limits of reactive penalties. According to Article 13(2-3) of this regulation, the reactive penalty limits are summarized in the table below.
| Penalty Type | Installed Power Penalty Limits | |
| < 50kVA | > 50kVA | |
| Inductive Reactive Limit | %33 | %20 |
| Capacitive Reactive Limit | %20 | %15 |
Customers with installed capacity below 50kVA will be penalized at the end of the month in the following cases:
- Çektikleri aktif enerjinin miktarının %33’ünden fazla endüktif reaktif enerji çekerlerse,
- %20’sinden fazla kapasitif reaktif enerji çekerlerse
Likewise, customers with installed power above 50kVA will also be subject to reactive penalty at the end of the month in the following cases:
- Çektikleri aktif enerjinin miktarının %20’sinden fazla endüktif reaktif enerji
- Ve/veya %15’inden fazla kapasitif reaktif enerji çekerlerse
As stated in Article 13(1) of the same regulation, if the reactive penalty limits are exceeded as a result of a malfunction in the reactive power compensation systems of consumers, the reactive energy consumption fee (i.e. reactive penalty) will not be invoiced once a year (calendar year).
So basically if we go into reactive punishment, we can cancel the reactive penalty once a year. The procedure for canceling a reactive penalty is twofold:
- Payment of the reactive penalty amount in cash by the distribution company to the customer
- Offsetting in the next month's invoice
Reactive Ratios
Reactive limits can be exceeded and penalized only for individual inductive or capacitive reactive energy consumption. Or both inductive and capacitive limits may be violated. In this case, the penalty is calculated based on the highest value on the inductive or capacitive side of the meter indices.
As is customary in electricity facilities, the reactive consumption rate or reactive penalty is calculated with the indices on the meter. Mostly, there is a staff member who follows these indices on a daily basis. The first thing he/she does when he/she arrives at the facility in the morning is to take the index from the meter. This personnel goes to the meter every morning and takes the indices of 1.8.0, 5.8.0 and 8.8.0. So, what do these indices mean to us?
- 1.8.0(T): Active energy consumption value (kWh)
- 5.8.0(Ri): Inductive reactive energy consumption value (kVArh)
- 8.8.0(Rc): Capacitive reactive energy consumption value (kVArh)
These values taken from the meter are compared with the previous day's values and the reactive energy status is monitored in this way. Let's make this more understandable with an example:
The values taken from the meter at one day intervals are summarized in the table below.
| Indices | 1.8.0(T): Active | 5.8.0(Ri): Inductive | 8.8.0(Rc): Capacitive |
| Last Index | 7689,265 | 1173,128 | 769,358 |
| First Index | 7523,125 | 1128,468 | 753,289 |
| Difference | 166,140 | 44,660 | 16,069 |
Compensation Power Calculation
This is how we can calculate reactive power ratios. So, using this data How do we calculate the necessary compensation power to get rid of the inductive reactive penalty?
In order to make this calculation, we need to have two more parameters other than the index values. These are the meter multiplier and the number of days the invoice is issued. This information can be easily found on the electricity bill.
Capacitor Power
In the light of the above data, it is necessary to compensate the inductive reactive power. condenser Let's calculate its power:
Meter Multiplier: 120, Billing Period: 30 days
Note: Since the indices are one day old, the billing period was taken as 1. If month-end indices are to be used, the invoicing period should be 30.
From the above calculations, we need 223.3kVAr of capacitor power to get rid of the inductive reactive charge/penalty with a rate of 26,86%. Since invoice-based compensation power calculations are average values, it would be more accurate to determine 10% more than the calculated value as the required compensation power. In this case, the required capacitor power can be determined as 245kVAr.
Example Case
Another invoice based calculation method is the calculation based on the target cosφ value. You can review the example below for this calculation method.
AP = Monthly average active power consumption (kWh) à 32100 kWh
AQ = Monthly average reactive power consumption (kVArh) à 49350 kVArh
cosφ2 = Target cosφ value à cosφ2 = 0.98 à tg φ2 = 0.2
t = Energy used per month (hours) à 260 hours
It is calculated as Since this value is also the average value, it will give a more accurate result to determine the 10% surplus as the required compensation power. In this case, the required capacitor power can be determined as approximately 185kVAr.
Another method is the calculation without using invoice parameters. This method can be used for existing facilities. For this, the installed power, demand power, current cosφ and target cosφ values of the existing facility must be known. You can also examine the example of the calculation made with this method below.
Installed Power 1200kW
Demand Power 1200 * 0.7 = 840kW
Value of cosφ1 at Demand Power = 0.82 à tgφ1 = 0.69
Target cosφ2 value = 0.98 à tgφ2 = 0.2
As the required capacitor power can be calculated.
Push Notifications with Reactive Alarms
Calculating the reactive rates of your business, calculating the reactive penalty, calculating the required compensation power is that simple. But as can be seen, a series of mathematical operations are performed. A dot or comma error in these operations can put things in an unmanageable situation. In addition, the slightest numerical error in the calculation of the data taken from the indices during hand calculation can cause additional problems.
Today, most of the existing plants use this way of tracking reactive consumption and calculating the required compensation power, and the mistakes mentioned above are often made. Well, what if there was an easier way of this monitoring, control and required power calculation.
How to Avoid Reactive Punishment?
Powered by artificial intelligence Apollochecks the status of the entire electrical system in your business and notifies you of possible problems instantly.
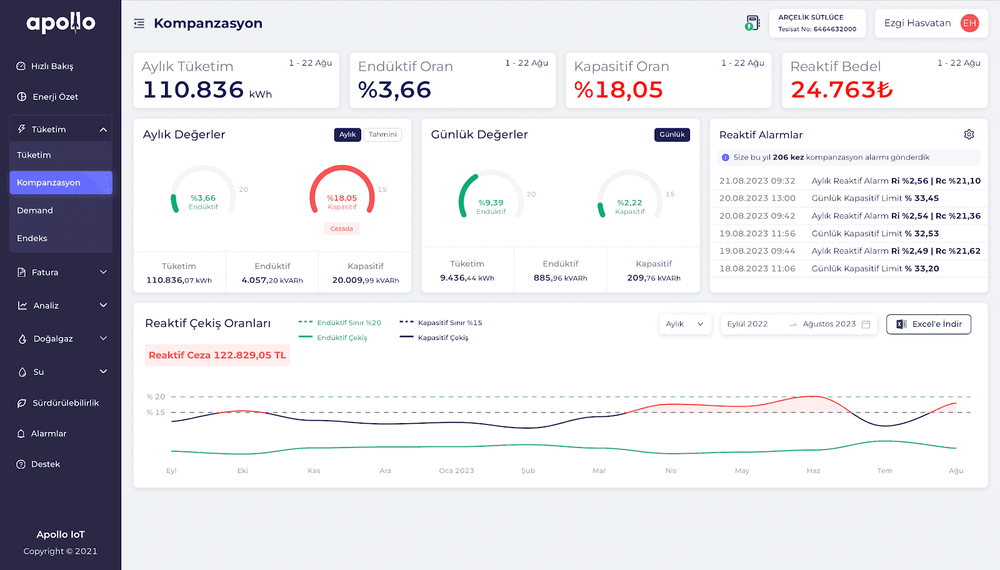
In addition, the required compensation power is presented to the users in kVAr as both inductive reactive power and capacitive reactive power. With the help of this feature, even the slightest change in the operating load profile or process does not go unnoticed and the required compensation power is immediately notified to the user by Apollo in order to prevent the reactive ratios from exceeding the specified limit values. In this way, Apollo prevents consumers from incurring reactive penalties.
Apollo ile Reaktif Ceza Maliyetlerinden Kurtul
Türkiye’nin ilk ve tek yapay zekâ tabalı yazılımı Apollo ile kompanzasyon takibi hiç olmadığı kadar kolay! Apollo ile elektrik faturalarının kontrolü, optimizasyonu ve tahminlemesini yapabilir, enerji tüketiminizin 365 derece takibini sağlayabilirsiniz.
With the Apollo platform, we offer you the opportunity to manage your energy without any infrastructure installation costs. We check your invoice with the data we receive automatically from the system or via modem. At the same time, we support you to plan your energy management correctly. We produce solutions for your company needs with regular innovations and update the portal. We can track raw material costs and reduce your energy consumption. Thus, we are happy to support you in pioneering a sustainable future.
To avoid reactive penalties, to manage your bills and energy correctly, to make the most efficient use of energy monitoring systems and to choose the most efficient electricity tariff deneyin.
You may also be interested in these topics:
Automatic Meter Reading System (OSOS): Revolutionizing Technology in Energy Management