SustainabilityIn today's rapidly changing world, sustainability cannot be considered only as an environmental responsibility. Sustainability aims to bring about a transformation by encompassing economic and social responsibilities along with the environment. Behaviors and cognitive interactions are shaped by the choices designers make and serve both our lives and a sustainable future. By recognizing critical points at the intersection between materials, production and design choices, design processes play a critical role in minimizing environmental impacts throughout the product lifecycle - from production to end-of-life. In this paper, we will explore the key strategies of sustainable design and discuss how they contribute to building a more sustainable future.
Circular Design Perspective
Traditional design approaches usually focus on the process of products and services after they reach the user. "End of Life (EoL)" while not addressing it, sustainable design and circular design strategies circular design replaces traditional design and offers a design approach that has been developed to include considerations such as ethics, equity and ecological impact. The circular design approach provides a change in thinking and a perspective that evaluates all processes throughout the life cycle of products and processes. Addressing the entire value chainIt enables effective decisions to be made at every stage of the design and thus maximum efficiency is achieved with minimum loss of value (waste, etc.).
Circular design strategies seek solutions to complex problems by drawing inspiration from nature, while system dynamics devaluating the product/process functionality importance is given. Thanks to this design perspective, instead of one-off solutions, the design process is placed at the center of the design process. sustainability it is possible to develop long-term sustainable solutions.
The structure of the linear economy model we are in directly explains why design is so important. The linear economy, which has so far often adopted the "take, use and discard" model, is not sustainable due to unlimited resources, limited financial means and lack of infrastructure. For these reasons, the transition to a circular economy is accelerating and the role of circular design is becoming increasingly important. Design is not only an aesthetic element, but also the key to creating a more environmentally, socially and economically efficient system. Design forms the fundamental building blocks of the transition from a linear to a circular economy model.
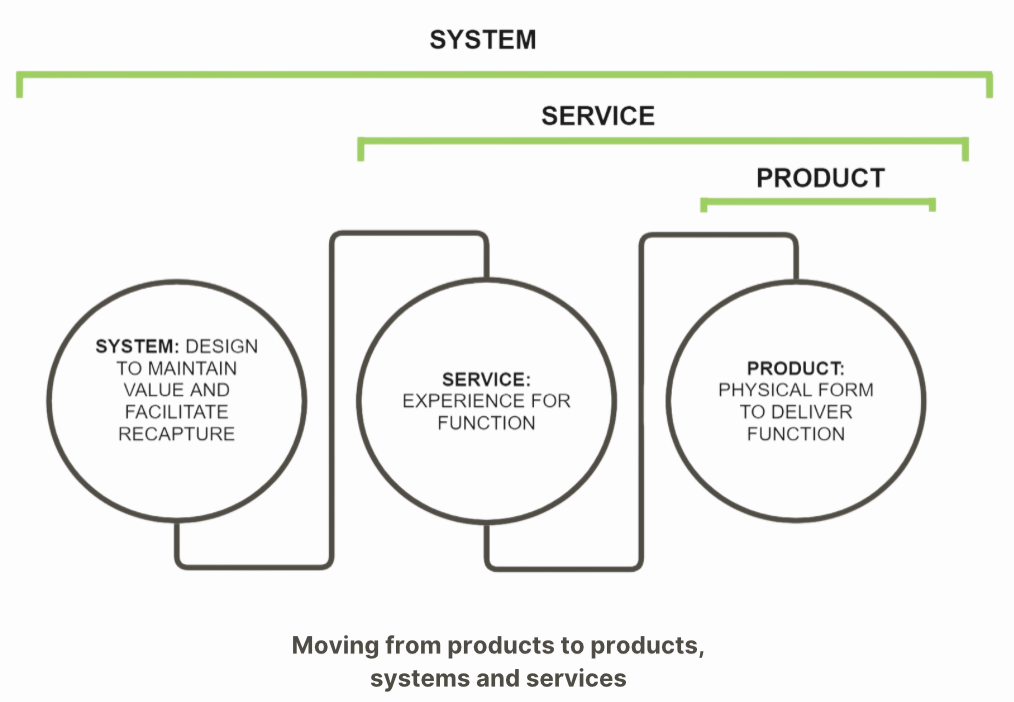
Product Service Systems Models
The PSS model aims at resource optimization by advocating the provision of products as a service, rather than focusing solely on the sale of products. Under this model, the manufacturer assumes responsibility for the entire life cycle of the product and aims to change its business model to make this possible.
Product represents a physical form and is usually a tangible item that fulfills a specific function. However Serviceincludes the provision of all services related to this product. That is, a product gains meaning not only through its physical presence, but also through the valuable services it provides to the user. These services include maintenance, repair, training and other support services throughout the lifetime of the product. A System is about products and services working together in an integrated way. Not only the product itself, but also all the services and processes through which it interacts with the user are part of this system. PSSThe aim is to make more efficient use of resources and reduce environmental impacts by offering products and services in an integrated way. This system combines the functionality of the product with the services that support it to meet the needs of the user, thus making products more valuable and efficient throughout their life cycle.
Producer Stewardship
It is an approach in which the manufacturer should take responsibility for the environmental impacts of the products throughout their entire life cycle; from design, to the production process, to the life cycle. With the help of the life cycle analysis (LCA) approach, environmental impacts should be taken into consideration during the design phase. LCA monitors not only the carbon footprint but also other environmental impacts such as water use in the entire life cycle of a product and shows manufacturers at which stages they can make improvements.
Tum through sustainable design strategiesDematerialization, material optimization (Dematerialization), use of materials with lower environmental impact, remanufacture, reusability, modularity and durability reshape product design to deliver environmental, economic and social benefits.
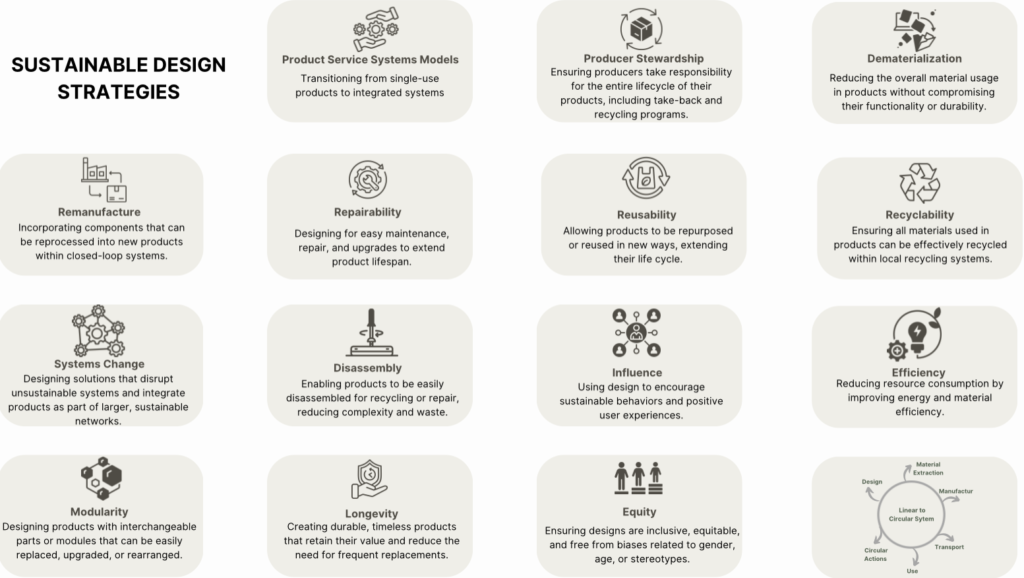
Apollo Ecowise'solutions offered byBy implementing these strategies, it helps you identify the environmental impacts of your products and processes, achieve carbon reduction, resource optimization and create roadmaps for your corporate sustainability goals. Start experimenting now!